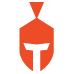
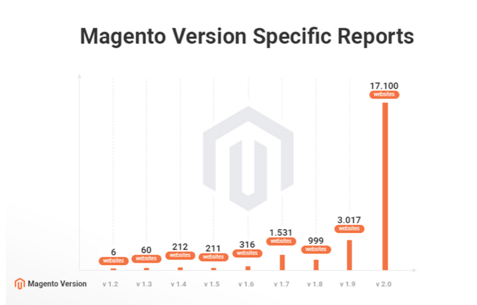
After Magento was released in 2008, it became the most popular e-commerce platform in the world. Magento’s expansion is increasing in a very impressive way. The number of sites hosted in Magento doubled between March 2017 and August 2018. Now a quarter of a million active e-commerce shops in Magento, and only 11,000 Magento sites have migrated to version 2. Magento announced the end of support of Magento1 to November 18, 2018, exactly 3 years after the Magento 2 release. But in September 2018, the team chose to postpone the date to June 2020.
No support means that these have no security updates, no bug fixes, and no more.
MIGRATING TO MAGENTO 2?
Adobe, the owner of Magento, has already taken many actions to motivate the merchants to migrate to Magento 2. The migration is therefore not natural. The entire code structure of Magento1 and Magento2 is very different. Therefore it is required to redevelop for achieving the same functionality. If Magento was the queen solution in the past years, then now the situation has changed with the appearance of a lot of competing solutions that have serious Arguments.
THE FUTURE OF E-COMMERCE PLATFORMS
At the same time, the web also underwent an evolutionary phase which made it adaptive to many service features that can be used by a site. Nowadays, monoliths are being replaced by microservices.
In SaaS all the services offered to communicate using APIs, thereby facilitating their interconnection, evolution, and even replacement. This made it more convenient than flat-file synchronizations. Separation of the backend from the frontend (user view) possess many advantages:
Assembling, Removing, Replacing third-party services are greatly facilitated. Specialized profiles are involved in each part. The frontend is unrelated to any business solution. This is much more adaptive and can also be updated and replaced independently. Thus, e-commerce engines which do not include the visitor theme part but a simple API that will deal with the functioning are often referred to as “headless”. For instance, Moltin or Spryker.
Javascript frameworks like Angular, React or VueJS are strong answers to this new way of framing its services on the “Frontend” part. The most beneficial point is their high speed in front end and they work with APIs. They are the ideal response to this microservice architecture since they are consistent with the PWA (Progressive Web App) standard set up by Google.
MAGENTO CAN BE INTEGRATED INTO THIS NEW DEAL
A front-end solution that connects to Magento 1 or 2 through its API to generate web pages itself and communicate directly with visitors is known as Front-Commerce. The core of the microservices architecture is the central connector (middleware), we deliver, which enables us to collect the different APIs (including Magento’s) to serve the theme (front) in a format optimized for integration: GraphQL.
Magento uses the unique “blank” theme, as the basis for all our projects, which is developed in React that allows incredible browsing speed, total freedom of layout, and PWA compatibility.
The e-merchant can now migrate some complex functionalities to detached microservices until he only has a “simple” e-commerce engine that can easily be replaced by another one when the time comes. Revolutionary change is that migrating to a new e-commerce solution supported by Front-Commerce (Magento 2, or another) will not require any change in the theme.
CONCLUSION
Magento has gone through many ups and downs so far. Magento has a strong future, despite being challenged by Shopify. Adobe’s acquisition has provided a massive boost. Also, the regular updates and patches are making it highly secure. So, in 2021, Magento may regain a significant number of lost users. It seems to be interesting to see how it fits against the other e-commerce platforms in the nearby future.